This page is a sub-page of our page on Linear Algebra.
///////
Related KMR pages:
• Shift of Basis for Vectors
• Shift of Basis for Linear Transformations
• Egenvalues and Eigenvectors
• Diagonalisation of Quadrics
///////
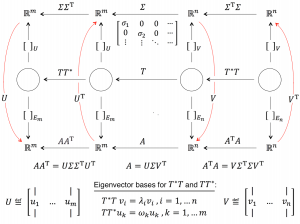
U \triangleq \begin{bmatrix} | & & | \\ u_1 & \cdots & u_m \\ | & & | \end{bmatrix}, \; V \triangleq \begin{bmatrix} \, | & & | \\ v_1 & \cdots & v_n \\ | & & | \end{bmatrix} .
T T^* u_k = {\omega}_k u_k \, , k=1, ... \,, m .
T^* T v_i = {\lambda}_i v_i \, , i=1, ...\,, n .
\Sigma = \begin{pmatrix} {\sigma}_1 & 0 & 0 & \cdots \\ 0 & {\sigma}_2 & 0 & \cdots \\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \cdots \end{pmatrix} .
A = U \Sigma V^\text{T} .
A A^\text{T} = U \Sigma {\Sigma}^\text{T} U^\text{T} .
A^\text{T} A = V {\Sigma}^\text{T} \Sigma V^\text{T} .
///////
Singular values decomposition
//////